All About Diamonds
4C’s of diamond
Cut

Determines how well the diamond reflects light, enhancing its sparkle. Grades range from Excellent to Poor.
Color
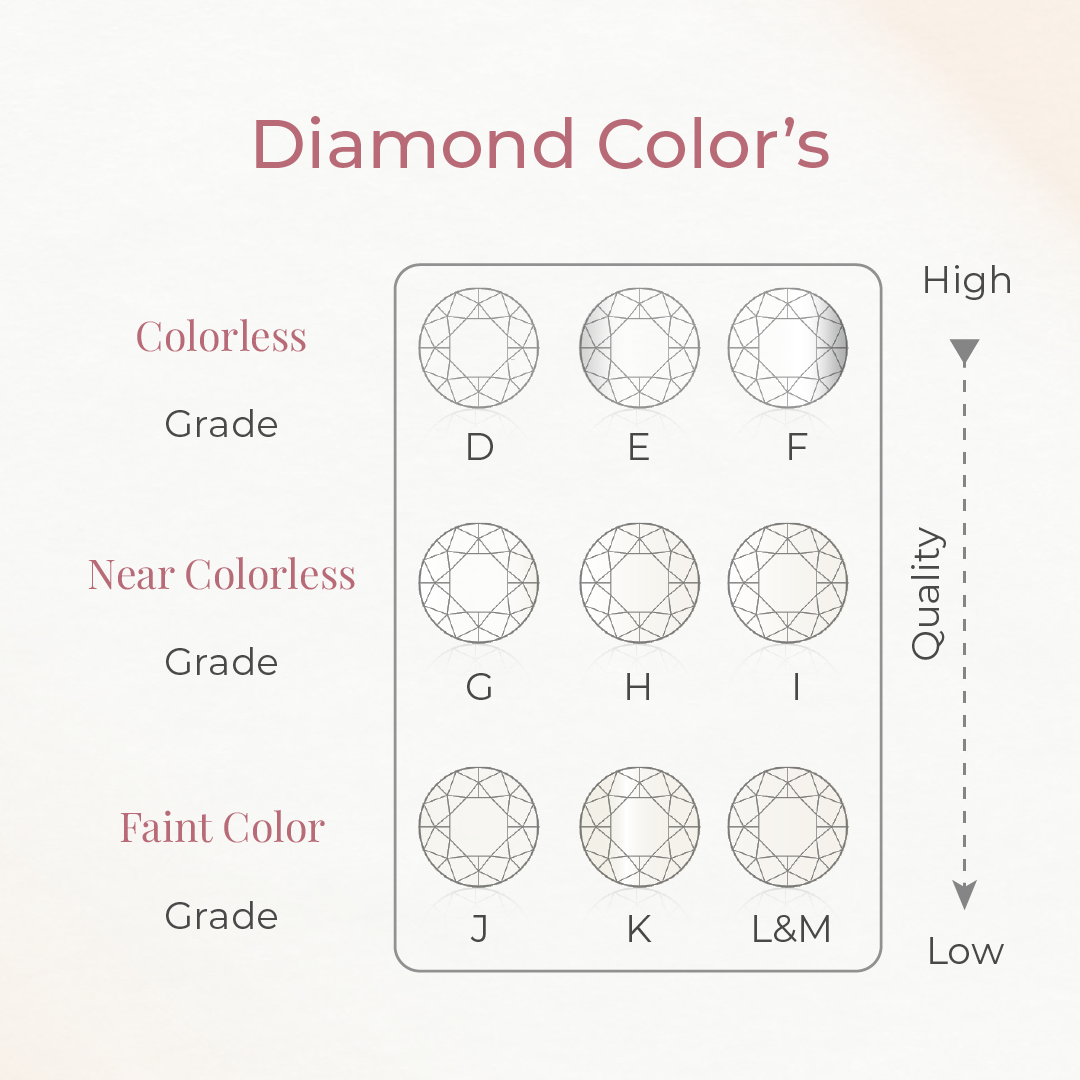
Graded from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow/brown). Colorless diamonds are rarer and more valuable
Clarity
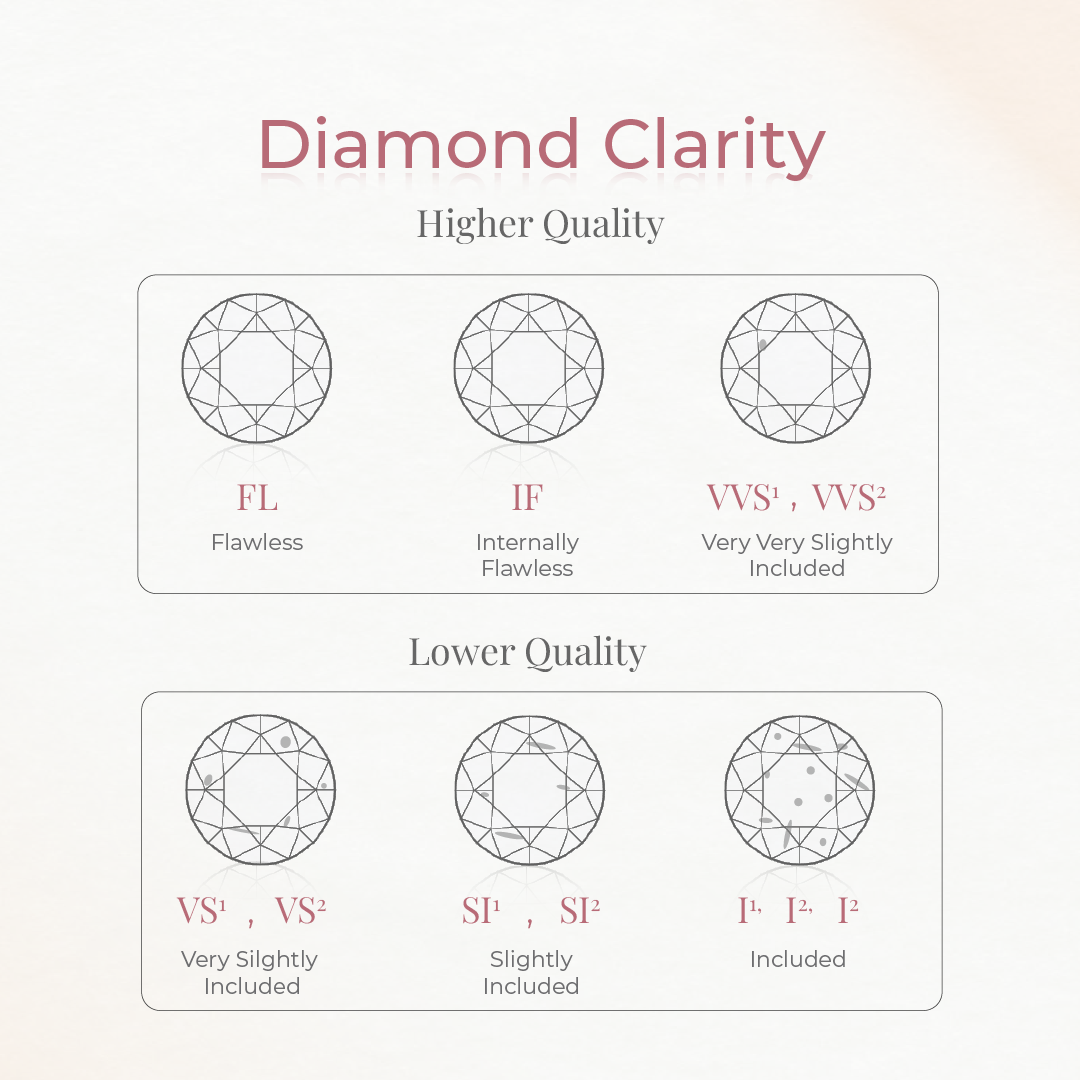
Measures internal flaws and surface imperfections. Clarity ranges from Flawless to Included, ensuring diamond purity.
Carat Weight
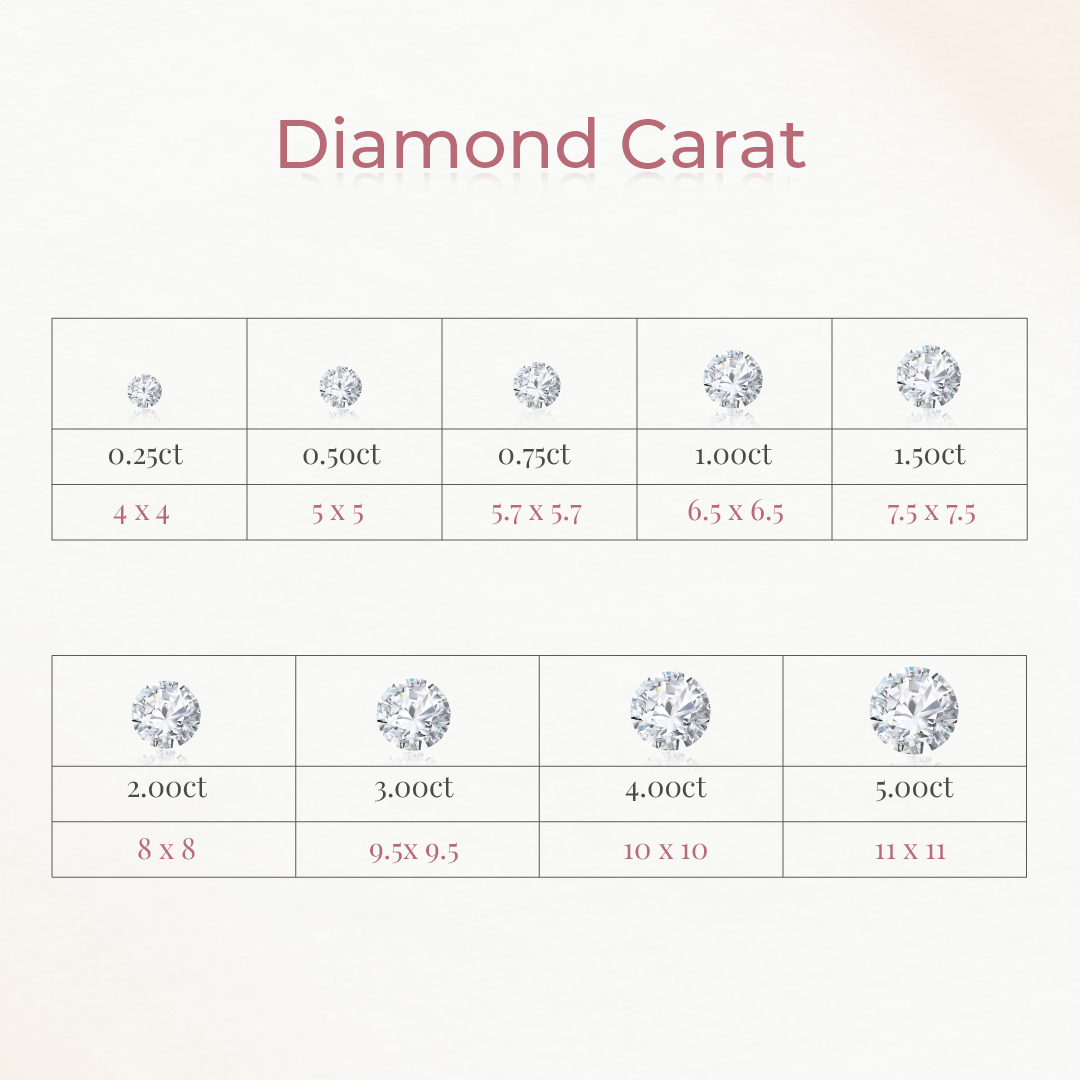
Refers to the size of the diamond. Larger diamonds are rarer and more valuable, but cut, color, and clarity also affect appearance.

A comprehensive guide to diamond characteristics that will help you purchase the right brilliance at the right price.
KNOW THE DIFFERENCE
Natural Diamond vs Lab Grown Diamond vs Moissanite Diamond

Natural Diamond
Formation: Formed over billions of years under Earth's mantle.
Uniqueness: Each is unique with distinct characteristics.
Value: More valuable due to rarity.
Environmental Impact: Mining impacts, though efforts for responsible practices exist.

Lab Grown Diamond
Formation: Created in labs with advanced technology.
Purity: Fewer inclusions, identical in composition to natural diamonds.
Value: More affordable with the same brilliance and quality.
Sustainability: Smaller carbon footprint and less environmental disruption.

Moissanite Diamond
Formation: Created in labs with advanced technology.
Purity: Fewer inclusions, identical in composition to natural diamonds.
Value: More affordable with the same brilliance and quality.
Sustainability: Smaller carbon footprint and less environmental disruption.
Moissanite Diamond
- More Affordable
- 9.25-9.5 on the Mohs hardness scale
- Rainbow-like light reflection
- Traditionally has yellow or green tint
- Ethically responsible
Natural Diamond
- For Most Expensive
- 10 on the Mohs hardness scale
- White light reflection
- Color range varies
- Ethically highly problematic
Lab Grown Diamond
- More Affordable
- 10 on the Mohs hardness scale
- White light reflection
- Color range varies
- Ethically Sustainable










